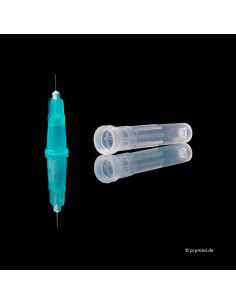
PRP tubes | Vi PRP-PRO | with Anticoagulant PU 10 pieces
The Vi PRP-Pro PRP tubes provide the fastest and most effective solution for the extraction and preparation of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) from patient blood – delivering outstanding results and maximum efficiency.
- Optimal blood release through specialized anticoagulant
- Minimizes clotting for precise results
- High quality for reliable PRP treatments
- Excellent cell separation and higher yield of platelet-rich plasma
- Maximum patient satisfaction through innovative technology
Order No. (PZN): 18354916
EAN number: 4170000035626